What Is Hybrid Electric Vehicle?
Topic: What is hybrid electric vehicle?


What Is Hybrid Electric Vehicle?
In simple terms, A hybrid blends at most one electric motor with an engine powered by gasoline to propel the vehicle, and it also reclaims energy by Regenerative brakes. Sometimes, the electric motor takes care of the entire work, but sometimes it’s the gasoline engine, and in other instances, they both work. This results in lower gasoline consumption and, consequently, better fuel efficiency. Electric power can improve performance in certain situations.
What Is Hybrid Electric Vehicle?
In all cases, the electricity is generated by the high-voltage battery pack (separate from the car’s traditional 12-volt battery), which is replenished through the capture of energy from deceleration. This energy is usually converted into heat by the brakes of conventional automobiles. (Regenerative braking systems accomplish this.) Hybrids also utilize fuel engines to recharge and maintain the battery. Automobile manufacturers employ different hybrid models to fulfil various goals, from maximizing fuel savings to keeping the cost of the car as low as is feasible.
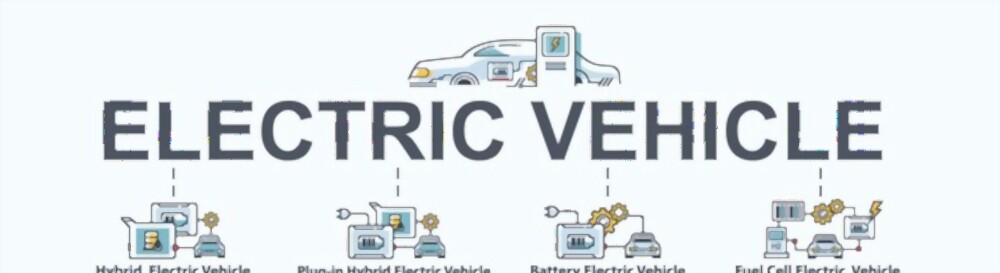

Types of Hybrid Vehicles
Parallel Hybrid
In this design, which is the most popular, it is the case that an electric motor(s) and the gasoline engine are linked through a common transmission that integrates both power sources. It could be manual, automatic, or a continuously variable transmission (CVT). One of the most popular hybrid transmissions is the power-split CVT employed in vehicles like the Toyota Prius and Chevrolet Volt. The type of transmission and dimensions of gasoline engines are major elements that determine how the parallel hybrid will speed up and sound and feel. The brands that utilize the parallel model include Toyota, Lexus, Hyundai, Kia, Ford, Honda, Lincoln, Nissan and Infiniti.
Series Hybrid
In this model, an electric motor(s) is the sole source of thrust; however, there isn’t an actual mechanical link between it and wheels. In this case, the gasoline-powered engine is used to charge the battery. This creates an experience of driving that’s more similar to an electric car that is smoother and has more strong acceleration. There’s usually less noise at the moment the gas engine is engaged. But, the engagement does not always occur in sync with what your left feet are doing (remember that the battery is taking the load), and the engine may be cranking up even though the car is moving at a constant speed. Some people find this to be a bit alarming. For instance, the BMW i3 equipped with an extended range can be an example of the series hybrid.
Plugin Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Plug-in hybrids improve the traditional hybrid model by utilizing a larger battery that, just like the electric car’s battery, needs to be fully charged by an external source of electricity, such as your workplace, home or even a public charging point. The larger amount of energy storage is similar to a bigger fuel tank. It permits extended electric driving (between 15 to 55 miles, depending on the type of vehicle) and could significantly cut down on gasoline consumption. If you’re on a short trip and recharge every night, it will be powered by electric power for the majority all the time. If you exhaust the battery, it will revert to a normal hybrid that is parallel. The Chrysler Pacifica plug-in hybrid (shown above) is an illustration of the plug-in hybrid breed.
Variations of The Hybrid Theme
Twenty years of innovation makes it even more difficult to determine “what is a hybrid?” Honda’s hybrid model is one example, but it doesn’t belong in the bucket of parallel or series. The engine is a generator for the majority of the time, similar to a series hybrid. However, at times it can be driven directly by the wheel, similar to an asymmetric hybrid. Also, there are hybrids on the road, such as the plug-in hybrids manufactured by Volvo that utilize a typical front-wheel-drive engine powered by an electric rear axle. These include the Acura NSX, BMW i8, and the Porsche 918 Spyder supercars are identical, except that their electric-only axles sit on the front.
Mild Hybrids
All of them are categorized as “full hybrids” in which the motor can drive the vehicle independently regardless of whether it’s only for a small distance. In the case of a “mild” hybrid, it is not able to. As a full hybrid, the electric motor serves to aid the gasoline engine to enhance efficiency, fuel efficiency, or both. It also acts as the start-up mechanism of the automatic stop-stop system that shuts down the engine once the vehicle stops for a time to reduce fuel consumption.
The idea was originally an easier and more affordable method to bring hybrid technology to the marketplace; the milder hybrids can’t enhance fuel efficiency in the same way that fully hybrids can. Therefore, they haven’t gained the same recognition. However, in recent years, light hybrid engines are making a comeback, as evidenced by the use of electrical subsystems with 48-volts in automobiles like those from the Ram 1500, Mercedes-Benz E-class, and Audi’s A7 as well as the A8. In essence, car manufacturers are now incorporating mild-hybrid technology into nearly every new car. Shortly, what will be the final answer for “what are hybrids?” could turn out to be “everything.”


Hybrid Electric Vehicle Battery
Storage systems for energy, most commonly batteries, are crucial in hybrid electric cars (HEVs) as well as Plug-in hybrid electric cars (PHEVs) and electric vehicles (EVs).
The majority of plug-in hybrids and all-electric vehicles are powered by lithium-ion batteries similar to these.
The following energy storage devices are utilized in HEVs, PHEVs, and EVs.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries can be found in most consumer electronics that are portable, like cell phones and laptops, due to their power density and high energy per unit of mass compared to other storage systems. They also have a superior power-to-weight ratio, high efficiency in energy use, excellent high-temperature performance, and low self-discharge. A majority of the lithium-ion battery components can be reused, but the expense of recycling remains a problem in the field. The U.S. Department of Energy is also assisting with the Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Award to discover ways of collecting, sorting, storage, and transporting the spent and old lithium-ion batteries for future recycling and recovery of materials. A majority of the current electric vehicles and electric vehicles utilize lithium-ion batteries; however, the exact chemistry is different from those for consumer electronics. Development and research areas are in progress to decrease these batteries’ cost, extend their life and resolve safety issues regarding overheating.
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
Nickel-metal-Hydride batteries, utilized often in medical and computer equipment, provide reasonable power and energy capabilities that are specific to. Nickel-metal Hydride batteries possess an extended life span than lead-acid batteries and are safe and tolerant of abuse. They are widely utilized to power PHEVs. The biggest issues associated with it nickel-metal hydride batteries are their high price, their high self-discharge and high heat production when temperatures are high, and the need to manage the loss of hydrogen.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries can be constructed to provide high power and are safe, inexpensive and reliable. However, the low specific energy, low cold-temperature performance, and a short cycle and calendar life limit their usage. The most advanced lead-acid batteries for high-power are in development; however, they’re only being used in electric-drive vehicles that are commercially available for load ancillary.
Ultracapacitors
Ultracapacitors store energy within a fluid that is polarized between electrodes and electrolytes. The capacity for energy storage increases as the size of the liquid’s surface grows. Ultracapacitors provide vehicles with additional power when they accelerate or are climbing and assist in recovering brake energy. They could also serve as a second energy storage device in electric-driven vehicles since they aid in the levelling load power levelling of electrochemical batteries.
Recycling Batteries
The electric-powered vehicle is relatively recent to this U.S. auto market, which means that only a tiny fraction of them have concluded their life span. This means that only a few post-consumer batteries of electric-drive vehicles are readily available, making it difficult to recycle batteries in the infrastructure. As electric-drive cars become more widespread, the market for battery recycling will likely grow.
Widespread recycling of batteries would prevent dangerous materials from entering the waste stream close to a battery’s lifespan and throughout its manufacturing. It is in the process of creating processes for recycling batteries that can reduce the impact on the life cycle of using lithium-ion and other types of batteries in automobiles. However, not all recycling methods are created equal:
- Smelting Processes that smelt help to recover essential components or salts. The processes are currently operating in large quantities and can take on various batteries, such as nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion. Smelting is performed at high temperatures—the organic materials, like carbon anodes and electrolytes are used as fuel or a reductant. The precious metals are reclaimed and then refined to make the product suitable for use in any situation. Other elements, such as lithium, are in the slag now utilized as an additive to concrete.
- Direct Recovery Direct recovery: On the other extreme, some recycling procedures direct recovery of battery-grade material. Components are separated through various chemical and physical processes, and all active materials and metals are recoverable. The direct recovery process is a low-temperature process that requires minimal energy.
- Intermediate processes The third kind of process falls between two extremes. These processes can accept various types of batteries but not direct recovery; however, they recuperate materials further in the chain of production in a way that smelting cannot.
Separating the various kinds of battery materials can be an obstacle in recovering the most valuable materials. Therefore, designing a battery that allows recycling and disassembly are crucial for electric vehicles to be successful from a sustainable perspective. The standardization of batteries, materials and cell design will facilitate recycling and be more affordable.
Full Hybrid Electric Vehicle
Full hybrids have larger batteries and more powerful electric motors, which can power the vehicle over short distances and at low speeds. These vehicles cost more than mild hybrids, but offer better fuel economy benefits.
Fully hybrid cars are able to travel (really) short distances on electricity alone. Again, it simply fills up and cranks up like any other normal vehicle, with the hybrid system automatically turning the engine on and off as needed, reducing fuel consumption where possible and delivering more power in the process.
Hybrid Electric Vehicle Kit
Flexible fleet solutions that are designed to help you transform your city’s fleet of trucks or buses. The revolutionary technology of regenerative brakes allows the iX HEV to transform the stop energy to electric charges. It harnesses the energy produced by the vehicle when the driver stops it. It stores it inside the battery box that is smart and utilizes this energy to propel the vehicle when it comes to a stop.
REGENERATIVE BRAKING Technology
The cutting-edge technology uses the energy generated by the stopping vehicle to create an electric charge that will then help power the vehicle.
AFFORDABLE BUT VIABLE
Our cutting-edge technology solutions ensure that retrofitting and recycling an old vehicle isn’t just less carbon-intensive than buying new ones; however, it is also much less expensive.
20 PERCENT FUEL COST REDUCTIONS
Our technology permits the reduction of up to 20% in fuel prices when compared to diesel. Savings pay back your investment in only 3-4 years.
Ideal FOR CITY LIFE
Semi-electric vehicles offer superior performance on routes that have an extremely high rate of acceleration and braking, for example, the intra-city bus and cargo routes. We provide you with a profitable return on your investment.
People Also Ask:
What are the components of a hybrid electric vehicle?
Regardless of the type of hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), the powertrain comprises at least the following elements: a drive motor; an electric motor with a DC-DC converter, a DC-AC inverter and the controller; an energy storage system (ESS); a transmission system.
Can I convert my car to a hybrid?
A conventional vehicle can be converted to a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) or a fully electric vehicle (EV). And an HEV can be converted to PHEV or EV. The systems used to convert vehicles to HEV and PHEV require certification from the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
How much does it cost to convert a vehicle to electric?
Once everything is installed and tested, the new electric car is ready to go! A typical conversion, if you use all of the new parts, costs between $ 5,000 and $ 10,000 (not including the cost of the donor’s vehicle or labour).
Can you drive a hybrid on electric only?
Hybrid cars are powered by a battery-electric motor and a gasoline or diesel internal combustion engine. Most will be able to drive with zero emissions (electric only), but the distance will depend on the size of the battery and whether you can plug it in to recharge it.
Is there an electric hybrid?
Hybrid electric vehicles are powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which uses energy stored in batteries. You cannot connect a hybrid electric vehicle to charge the battery. The battery can also power auxiliary loads and reduce engine idling when stationary.
What is the difference between a mild hybrid and a full hybrid?
All hybrid cars are powered by a combination of internal combustion engine and electric motors. Lightweight hybrid cars only use their electric motors to support the engine during acceleration and cruising; the electric motor cannot drive the car by itself.
What is difference between a fully electric vehicle and a hybrid vehicle?
We often hear about different models of electric or hybrid cars, but they are not the same. The fundamental difference between the two is that an electric car runs exclusively on electrical energy stored in a battery, while a hybrid car runs on a combination of electricity and conventional fuel.
Is a hybrid fully electric?
Hybrid electric vehicles are powered by an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which uses energy stored in batteries. You cannot connect a hybrid electric vehicle to charge the battery. Instead, the battery is charged by regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine.
Recommended Article:
How Long Does It Take To Charge A Tesla?
Electric Van That Could Use Solar Panels
Tesla Autopilot with Convenience Features
How to become electric car mechanic training?






[…] diesel or petrol engine vehicles, the energy consumption of electric vehicles’ energy consumption depends on the model and manufacturer. We don’t talk about “litres […]
[…] trend in the automobile industry, and the rapid rate of change is unlikely to cease very soon. As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity due to their low energy usage and inexpensive cost, the complexity of […]
[…] all drivers realise that parking places at charging stations are reserved only for plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) to make the most efficient use of the […]
[…] is used in conjunction with one or more electric motors, drawing power from batteries to power the hybrid electric vehicle. A mild hybrid—also known as micro hybrids—can reduce fuel consumption when the vehicle is […]
[…] fleet-only special, the Q-Series electric vehicle is now available to a small number of hand-picked fleets. As a result, only 70 units have been sold […]
[…] announcing today that by 2030, the majority of the vehicles we sell will be electric and that these vehicles will exemplify our distinctive take on contemporary Japanese luxury. […]
[…] autonomy: Alke’ ATX electric vehicles offer an autonomy of up to 200 km WLTP and, thanks to an approved fifth wheel, can be used with […]
[…] general, electric vehicles require less upkeep than traditional automobiles […]
[…] to Aki Marceau, Hawaiian Electric’s director of electrification for transportation, more drivers will switch to electri… when a dependable and convenient EV charging infrastructure is in place. By switching to electric […]
[…] gas emissions could be reduced by using electric automobiles. Research on electric vehicles and their charging infrastructure has been considerable; nonetheless, there is still a lot of room […]
[…] controller’s role in a DC electric vehicle is straightforward. Assume the battery pack comprises 12 12-volt batteries connected to provide 144 […]
[…] second element is that there is no appropriate ecology for buyers to use an Electric Vehicle without difficulty. When I say “ecosystem,” I’m talking to the charging stations […]
[…] energy system, driving an electric automobile is a terrific method to promote sustainable energy. Electric vehicles have gone a long way in recent years, virtually doubling their range from roughly 73 miles per […]
[…] 2010, I’ve been driving electric cars and working with several manufacturers on electric vehicle development. How do automobiles perform in the winter? This is one of the most often requested […]
[…] use energy stored in batteries to power hybrid electric vehicles. It is not possible to plug in a hybrid electric vehicle. Rather, the batteries are charged by the car’s motor and […]
[…] you like the brand or loathe it, the brand has been a huge help to the auto industry. It has made electric vehicles an issue of conversation, and something competitors are now […]